Mastering Firebase for Android Apps
Introduction
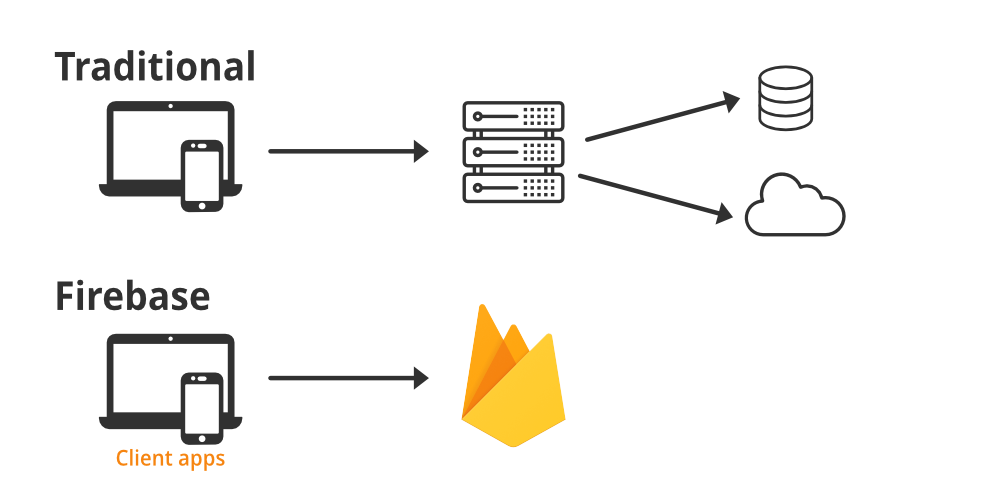
Firebase, a platform developed by Google, is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to help you build, improve, and grow your app. Whether you are a novice developer or an experienced programmer, Firebase offers a range of functionalities that can simplify and enhance your Android app development process. In this blog, we will dive into how to master Firebase for Android apps, covering its core components, integration steps, and best practices.
Why Firebase?
Firebase provides a unified platform that integrates various services like real-time databases, authentication, cloud storage, and analytics. This allows developers to focus more on building features rather than setting up infrastructure.
Key Components of Firebase
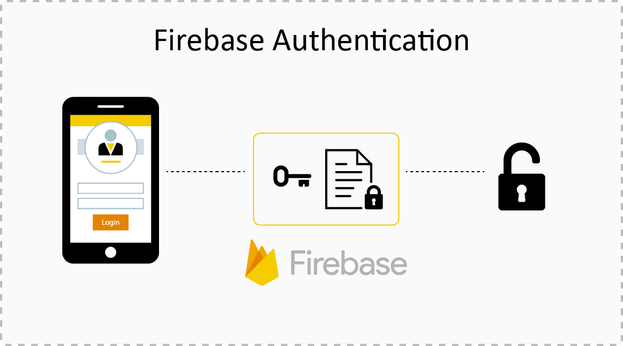
Firebase Authentication
- Simplifies user authentication with support for email, Google, Facebook, and other providers.
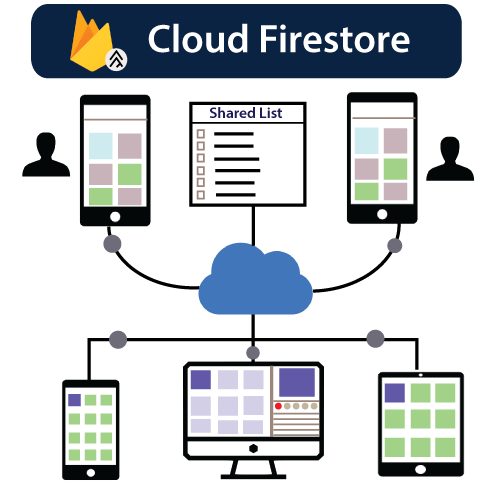
Firebase Realtime Database & Firestore
- Offers real-time synchronization of data across all clients, making it ideal for chat applications, live updates, etc.
- Firestore, a more scalable and flexible database, supports more complex queries and structures.
Firebase Cloud Storage
- Provides secure file uploads and downloads for user-generated content such as images, videos, and other files.
Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM)
- Enables push notifications to engage users and keep them informed about app updates or messages.
Firebase Analytics
- Offers detailed insights into user behavior and engagement, helping you make informed decisions about your app's future development.
Getting Started with Firebase for Android
Step 1: Create a Firebase Project
- Go to the Firebase Console.
- Click on "Add project" and follow the prompts to create a new project.
Step 2: Add Firebase to Your Android Project
Register your app with Firebase by entering the package name.
Download the
google-services.jsonfile and place it in theappdirectory of your Android project.Add the Firebase SDK to your
build.gradlefiles:
// In the project-level build.gradle filebuildscript {dependencies {classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.10' // Check for the latest version}}// In the app-level build.gradle fileapply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'dependencies {implementation platform('com.google.firebase:firebase-bom:29.0.4') // Check for the latest versionimplementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-analytics'// Add other Firebase dependencies as needed}
Step 3: Initialize Firebase in Your App
In your
MainActivityor a customApplicationclass, initialize Firebase:
import com.google.firebase.FirebaseApp;
public class MyApp extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
FirebaseApp.initializeApp(this);
}
}
Using Firebase Authentication
To implement Firebase Authentication:
Enable the desired authentication method in the Firebase Console.
Add the authentication dependency to yourbuild.gradlefile:
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-auth'3. Write code to handle user sign-up and sign-in:FirebaseAuth mAuth = FirebaseAuth.getInstance();// Sign up a new usermAuth.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(email, password).addOnCompleteListener(this, task -> {if (task.isSuccessful()) {FirebaseUser user = mAuth.getCurrentUser();// Update UI with the signed-in user's information} else {// If sign-in fails, display a message to the user.}});// Sign in an existing usermAuth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email, password).addOnCompleteListener(this, task -> {if (task.isSuccessful()) {FirebaseUser user = mAuth.getCurrentUser();// Update UI with the signed-in user's information} else {// If sign-in fails, display a message to the user.}});Real-Time Database & Firestore
Add the database dependency:Realtime Database
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-database'2. Read and write data:DatabaseReference myRef = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance().getReference("message");// Write datamyRef.setValue("Hello, World!");// Read datamyRef.addValueEventListener(new ValueEventListener() {@Overridepublic void onDataChange(DataSnapshot dataSnapshot) {String value = dataSnapshot.getValue(String.class);// Update UI with the data}@Overridepublic void onCancelled(DatabaseError error) {// Failed to read value}});
Firestore
Add the Firestore dependency:implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-firestore'2. Read and write data:FirebaseFirestore db = FirebaseFirestore.getInstance();// Create a new user with a first and last nameMap<String, Object> user = new HashMap<>();user.put("first", "Ada");user.put("last", "Lovelace");// Add a new document with a generated IDdb.collection("users").add(user).addOnSuccessListener(documentReference -> {// Document added successfully}).addOnFailureListener(e -> {// Error adding document});// Read datadb.collection("users").get().addOnCompleteListener(task -> {if (task.isSuccessful()) {for (QueryDocumentSnapshot document : task.getResult()) {// Retrieve and display data}} else {// Error getting documents}});Best Practices
- Security Rules: Always set up proper security rules in the Firebase Console to protect your data.
- Offline Capabilities: Use Firebase's offline features to enhance user experience when there is no internet connection.
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling to manage failures gracefully.
- Analytics: Use Firebase Analytics to track user interactions and understand their behavior within your app.
Conclusion
Firebase offers a powerful set of tools that can significantly accelerate your Android app development process. By mastering Firebase, you can create more robust, scalable, and feature-rich applications. Whether you are working on user authentication, real-time data synchronization, or push notifications, Firebase provides the solutions you need. Happy coding!



Comments
Post a Comment